Migraines vs. Headaches: Understanding the Difference
We’ve all experienced headaches at some point in our lives, but not all headaches are created equal. Some people use the terms migraine and headache interchangeably, but they are actually quite different in their causes, symptoms, and treatments. Knowing the difference can help you manage your pain effectively and seek the right treatment when needed (Cleveland Clinic, 2023).
What is a Headache?
A headache is a broad term that refers to pain in the head, scalp, or neck. It can be caused by various factors, including stress, dehydration, lack of sleep, eye strain, or even certain foods (Mayo Clinic, 2023). There are several types of headaches, including:
- Tension Headaches – The most common type, often caused by stress or muscle tension. They usually feel like a dull, aching pain around the forehead or the back of the head.
- Cluster Headaches – Intense headaches that occur in clusters over weeks or months, often causing severe pain around one eye.
- Sinus Headaches – Caused by sinus infections or allergies, leading to pressure and pain around the forehead, cheeks, and nose.
- Exertion Headaches – Triggered by physical activity, such as exercise or coughing.
Headaches are generally short-lived and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, hydration, rest, and relaxation techniques (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke [NINDS], 2023).

What is a Migraine?
A migraine is more than just a bad headache—it’s a neurological condition that comes with a range of symptoms beyond head pain. Migraines often occur in phases and can last for hours to days (American Migraine Foundation, 2023). Common symptoms of migraines include:
- Throbbing or Pulsating Pain – Usually on one side of the head but can affect both.
- Nausea and Vomiting – Many people with migraines experience digestive issues.
- Sensitivity to Light and Sound – Bright lights and loud noises can worsen symptoms.
- Aura – Some individuals experience visual disturbances, such as flashing lights or blind spots, before the migraine begins.
- Fatigue and Brain Fog – Migraines can leave you feeling exhausted and mentally drained even after the pain subsides.
Triggers for migraines can include stress, hormonal changes, lack of sleep, certain foods (like caffeine, alcohol, or processed meats), weather changes, and sensory stimuli (Mayo Clinic, 2023).

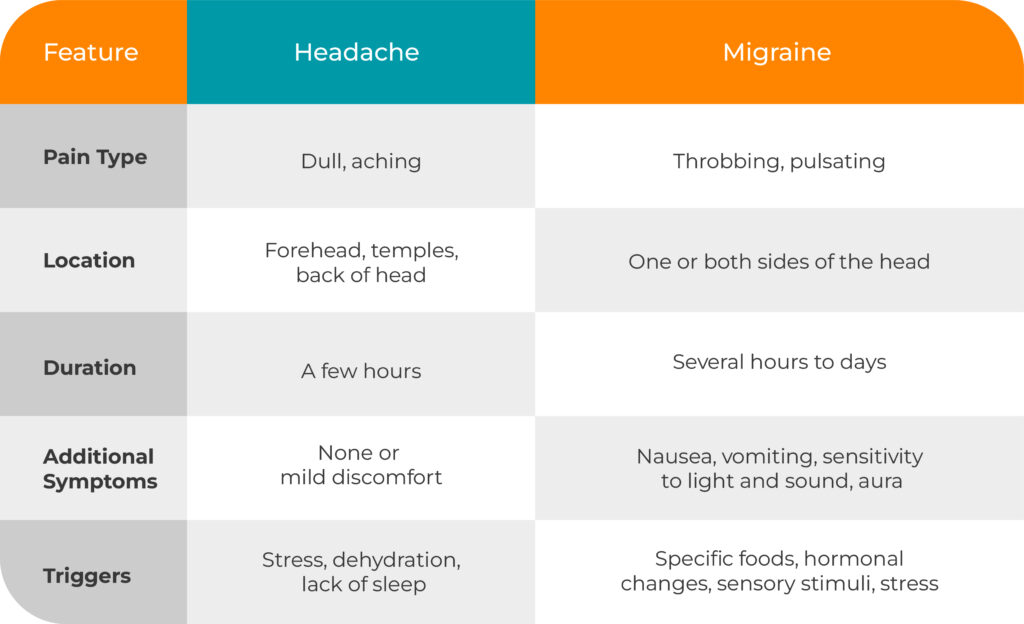
How to Tell the Difference?
The key differences between headaches and migraines lie in their symptoms, duration, and severity. Recognizing these differences can help with faster relief and better long-term management (Cleveland Clinic, 2023).
Treatment and Prevention
- Headaches: Can often be relieved with rest, hydration, stress management, and pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Migraines: Treatment may include prescription medications, lifestyle changes, avoiding triggers, and in some cases, preventive medications prescribed by a doctor (American Migraine Foundation, 2023).

When to See a Doctor
If you experience frequent, severe, or unusual headaches, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Seek immediate medical attention if your headache is sudden and severe, accompanied by confusion, weakness, vision loss, or other neurological symptoms (NINDS, 2023).
Understanding the difference between a migraine and a headache can help you take the right steps to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. If you’re unsure what you’re dealing with, keeping a headache diary to track your symptoms and triggers can be a helpful tool in finding the best treatment plan (Mayo Clinic, 2023).

References
American Migraine Foundation. (2023). Migraine 101: What you need to know. https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/resource-library/migraine-101/
Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Headache vs. migraine: What’s the difference? https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9639-headaches
Mayo Clinic. (2023). Headache. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/headache/symptoms-causes/syc-20361730
Mayo Clinic. (2023). Migraine. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/symptoms-causes/syc-20360201
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2023). Headache: Hope through research. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/headache




