A Smarter Way to Treat Pain: How to Avoid the Side Effects of Advil
Advil (ibuprofen) is a common go-to for pain relief, but it’s not always the best option for everyone. While effective, it can cause side effects like stomach irritation, ulcers, and increased blood pressure (Mayo Clinic, 2024). But did you know there’s a way to relieve pain while avoiding these risks?
The Topical Alternative
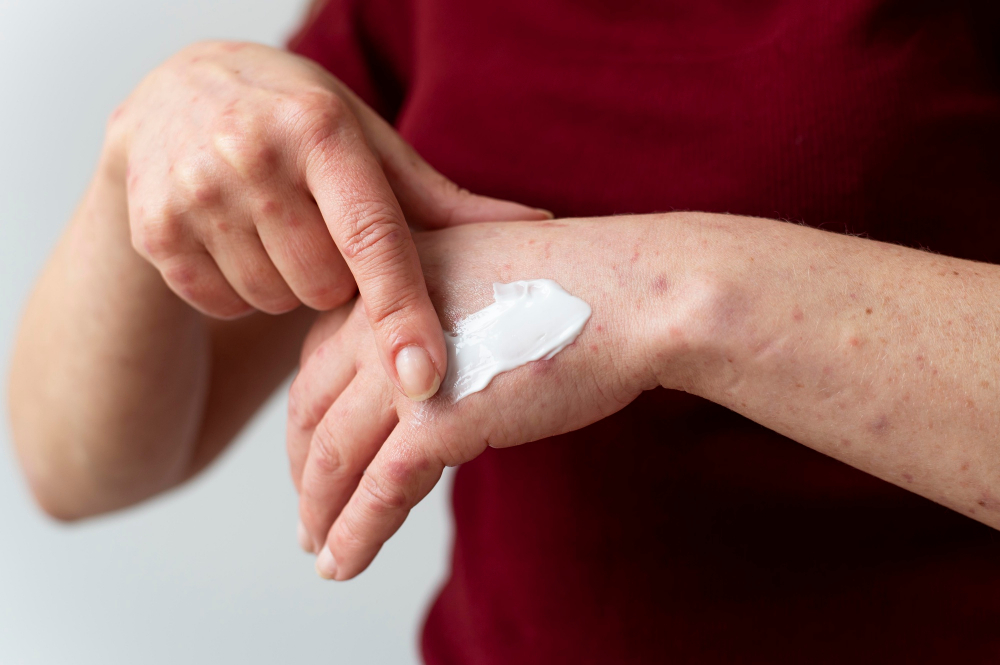
Instead of taking an oral anti-inflammatory like Advil, you can use a topical anti-inflammatory cream. These creams deliver pain relief directly to the affected area without affecting your entire body. That means:
✅ Less risk of stomach upset and ulcers (Cleveland Clinic, 2023)
✅ No impact on blood pressure (American Heart Association, 2024)
✅ Targeted relief at the source of pain
Why It Works
When you take an oral NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) like ibuprofen, it enters your bloodstream and circulates throughout your body. This systemic effect is what leads to side effects like gastrointestinal irritation, kidney stress, and blood pressure elevation (Harvard Health, 2023).
Topical NSAIDs, on the other hand, work locally. When applied to the skin, they penetrate the underlying tissues to reduce inflammation without reaching high levels in the bloodstream (National Institutes of Health, 2023).
When to Use (And When Not To)
While topical anti-inflammatories are great for muscle pain and osteoarthritis, they have some limitations:
- ✅ Best for pain close to the surface, such as joint pain, tendonitis, and muscle soreness (Arthritis Foundation, 2024).
- ❌ Less effective for deep-seated pain, like severe back pain or internal injuries.
For conditions like osteoarthritis, studies have shown that topical NSAIDs like diclofenac gel can be just as effective as oral NSAIDs—but with fewer side effects (BMJ Open, 2022).

Final Thoughts
If Advil upsets your stomach or raises your blood pressure, consider switching to a topical anti-inflammatory. It’s an effective way to target pain while protecting your overall health. Always follow usage instructions and check with your pharmacist or doctor if you have any concerns.
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). NSAIDs: Risks and Side Effects. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). How NSAIDs Affect the Stomach. Retrieved from https://www.clevelandclinic.org
- American Heart Association. (2024). NSAIDs and Blood Pressure: What You Need to Know. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org
- Harvard Health. (2023). Understanding NSAID Risks. Retrieved from https://www.health.harvard.edu
- National Institutes of Health. (2023). Topical NSAIDs: Benefits and Limitations. Retrieved from https://www.nih.gov
- Arthritis Foundation. (2024). Topical Treatments for Joint Pain. Retrieved from https://www.arthritis.org
- BMJ Open. (2022). Efficacy and Safety of Topical NSAIDs in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Retrieved from https://bmjopen.bmj.com




